1. Write a C++ program to add element in the stack and print the top element.
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//create a stack of strings
stack<string> prog;
//add element to the Stack
prog.push(“C”);
prog.push(“C++”);
prog.push(“Java”);
prog.push(“Python”);
//print top element
cout<<prog.top();
}
Output:
Python
2. Write a C++ program to add element in the stack, remove element and print the stack element.
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int>st;
st.push(11);
st.push(12);
st.push(13);
st.push(14);
int num=10;
st.push(num);
st.pop();
st.pop();
st.pop();
while(!st.empty()) {
cout<<st.top()<<” “;
st.pop();
}
}
Output:
12 11
3. Write a C program to add element into the Stack
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//create a stack of strings
stack<string> colors;
//push elements into the stack
colors.push(“Red”);
colors.push(“Blue”);
colors.push(“Green”);
colors.push(“Black”);
//print elements of stack
while(!colors.empty()) {
cout << colors.top() << ” “;
colors.pop();
}
}
Output:
Black Green Blue Red
4. Write a program in C++ to access elements from the Stack
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//create a stack of strings
stack<string> colors;
//push element into the stack
colors.push(“Red”);
colors.push(“Green”);
colors.push(“Blue”);
colors.push(“Orange”);
colors.push(“Purple”);
//get top element
string top = colors.top();
cout <<“Top Element: ” <<top;
}
Output:
Top Element: Purple
5. Write a C++ program to get the size of the Stack
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//create a stack of int
stack<int> prime;
//push elements into the stack
prime.push(2);
prime.push(3);
prime.push(5);
prime.push(7);
//get the size of the stack
int size = prime.size();
cout<<“Size of the stack: ” << size;
}
Output:
Size of the stack: 4
6. Write a C++ program to check if the Stack is Empty
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//create a stack of double
stack<double>nums;
cout<<“Is the stack empty?”;
if(nums.empty()) {
cout<<“Yes”<<endl;
}
else {
cout<<“No”<<endl;
}
cout<<“Pushing elements…”;
nums.push(2.3);
nums.push(9.7);
cout<<endl<<“Is the stack empty?”;
if(nums.empty()) {
cout<<“Yes”;
}
else {
cout<<“No”;
}
}
Output:
Is the stack empty? Yes
Pushing elements…
Is the stack empty? No
7. Write a simple C++ program to show the use of basic stack functions.
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
void displaystack(stack <int> st)
{
while (!st.empty())
{
cout <<” “<<st.top();
st.pop();
}
cout << ‘\n’;
}
int main ()
{
stack <int> st;
st.push(55);
st.push(44);
st.push(33);
st.push(22);
st.push(11);
cout <<“The stack is: “;
displaystack(st);
cout <<“\nSize of the stack:” <<st.size();
cout<<“\nTop element of the stack: ” <<st.top();
}
Output:
The stack is : 11 22 33 44 55
Size of the stack: 5
Top element of the stack : 11
8. Write a program in C++ to remove elements from the stack
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
void display_stack(stack<string> colors) {
while(!colors.empty()) {
cout <<colors.top() << ” “;
colors.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
//create a stack of strings
stack<string> colors;
//push elements into the stack
colors.push(“Red”);
colors.push(“Green”);
colors.push(“Blue”);
colors.push(“Orange”);
colors.push(“Purple”);
colors.push(“Black”);
cout<<“Initial Stack: “;
// print elements of stack
display_stack(colors);
// removes 2 elements from the stack
colors.pop();
colors.pop();
cout<<“Final Stack: “;
// print elements of stack
display_stack(colors);
}
Output:
Initial Stack: Black Purple Orange Blue Green Red
Final Stack: Orange Blue Green Red
9. Write a C++ program to implement stack using array.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int stack[10], n=10, top=-1;
void push(int val) {
if(top>=n–1)
cout<<“Stack Overflow”<<endl;
else {
top++;
stack[top]=val;
}
}
void pop() {
if(top<=-1)
cout<<“Stack Underflow”<<endl;
else {
cout<<“The popped element is: “<< stack[top] <<endl;
top—;
}
}
void display() {
if(top>=0) {
cout<<“Stack elements are:”;
for(int i=top; i>=0; i—)
cout<<stack[i]<<” “;
cout<<endl;
} else
cout<<“Stack is empty”;
}
int main() {
int ch, val;
cout<<“1) Push”<<endl;
cout<<“2) Pop”<<endl;
cout<<“3) Display”<<endl;
cout<<“4) Exit”<<endl;
do {
cout<<“Enter choice: “;
cin>>ch;
switch(ch) {
case 1: {
cout<<“Enter value to be pushed: “;
cin>>val;
push(val);
break;
}
case 2: {
pop();
break;
}
case 3: {
display();
break;
}
case 4: {
cout<<“Exit”<<endl;
break;
}
default: {
cout<<“Invalid Choice”<<endl;
}
}
}while(ch!=4);
return 0;
}
Output:
1) Push
2) Pop
3) Display
4) Exit
Enter choice: 1
Enter value to be pushed: 2
Enter choice: 3
Stack elements are:2
Enter choice: 1
Enter value to be pushed: 4
Enter choice: 5
Invalid Choice
Enter choice: 1
Enter value to be pushed: 6
Enter choice: 1
Enter value to be pushed: 7
Enter choice: 2
The popped element is: 7
Enter choice: 2
The popped element is: 6
Enter choice: 3
Stack elements are:4 2
Enter choice: 4
Exit
9. Write a C++ program to implement a stack using an array with push and pop operations. Find the top element of the stack and check if the stack is empty or not.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100 // Maximum size of stack
int stack[MAX], top=-1;
void push(int val) {
if(top>=MAX-1)
cout<<“Stack is Full”<<endl;
else {
top ++;
stack[top]=val;
}
}
void pop() {
if(top<0)
cout<<“Stack Underflow”<<endl;
else {
cout<<“\nThe popped element is: “<< stack[top] <<endl;
top –;
}
}
int peek() {
if (top < 0) {
cout << “Stack is empty” << endl; // Display message if stack is empty
}
else
return stack[top]; // Return top element without modifying top index
}
//Check the stack is empty or not
void isEmpty() {
if (top<0) {
cout <<“Yes”<< endl;}
else {
cout<<“No”;
}
}
void display() {
if(top>=0) {
cout<<“Stack elements are:”;
for(int i=top; i>=0; i–)
cout<<stack[i]<<” “;
cout<<endl;
}
else
cout<<“Stack is empty”;
}
int main() {
cout <<“If the stack is empty ? “;
isEmpty();
cout <<“\nInsert elements in the stack…\n”;
push(7);
push(6);
push(5);
push(4);
display(); // Display elements in the stack
cout << “\nRemove an element from the stack….”;
pop(); // Pop an element from the stack
display(); // Display elements in the stack
cout << “\nTop element of the stack: “;
cout <<peek(); // Display the top element of the stack
cout << endl;
}
Output:
If the stack is empty ? Yes
Insert elements in the stack…
Stack elements are:4 5 6 7
Remove an element from the stack….
The popped element is: 4
Stack elements are:5 6 7
Top element of the stack: 5
10. Write a program to implement stack through class and objects.
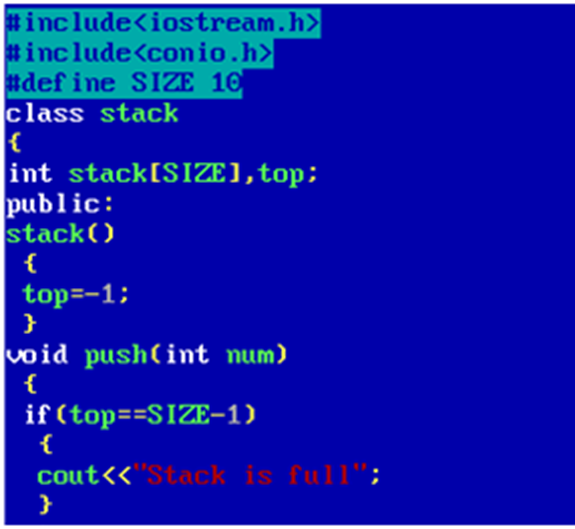
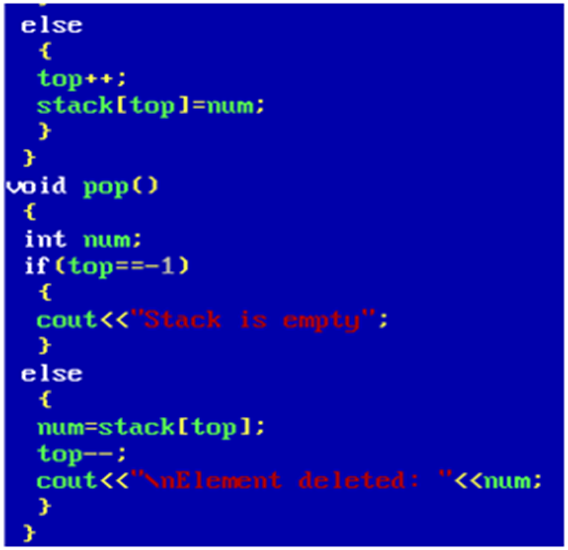
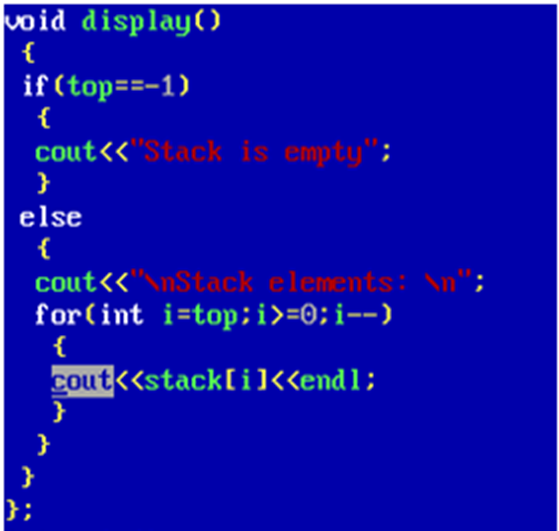
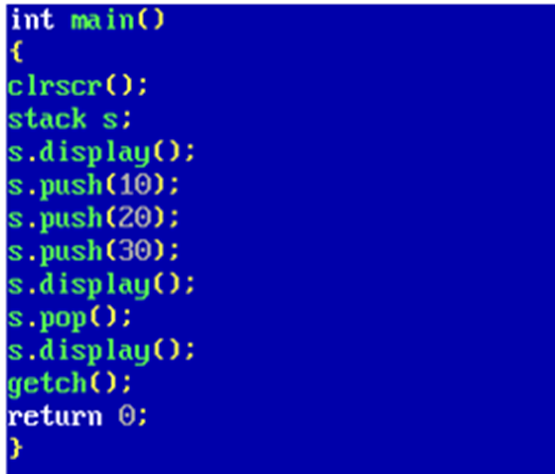
Output:
10. Write a C++ program to implement a stack using an array with push and pop operations. Check if the stack is full.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 5 // Maximum size of stack
class Stack {
private:
int top; // Index of top element
int st[MAX]; // Array to store elements
public:
Stack() {
top = -1; // Initialize top index to -1 (empty stack)
}
bool push(int x) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << “Stack overflow” << endl; // Display message if stack is full
return false; // Return false to indicate failure in pushing element
}
st[++top] = x; // Increment top index and add element to array
return true; // Return true to indicate successful element addition
}
int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << “Stack underflow” << endl; // Display message if stack is empty
return 0; // Return 0 to indicate failure in popping element
}
return st[top–]; // Return top element and decrement top index
}
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << “Stack is empty” << endl; // Display message if stack is empty
return 0; // Return 0 to indicate failure in peeking element
}
return st[top]; // Return top element without modifying top index
}
bool isEmpty() {
return (top < 0); // Return true if stack is empty (top index is -1)
}
bool isFull() {
return (top >= MAX- 1); // Return true if stack is full (top index is equal to MAX – 1)
}
void display() {
if (top < 0) {
cout <<“Stack is empty”<<endl;
return;
}
cout << “\nStack elements: “;
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i–)
cout <<st[i] <<” “;
cout << endl;
}
};
int main() {
cout << “MAX SIZE of the array: ” <<MAX;
// Initialize a stack
Stack s;
cout << “\nInsert elements in the stack:\n”;
s.push(5);
s.push(4);
s.push(3);
s.push(2);
s.push(1);
s.display(); // Display elements in the stack
cout << “Is the stack full? ” << s.isFull() << endl; // Check if the stack is full
cout << “\nRemove an element from the stack: “;
cout << s.pop();
s.display(); // Display elements in the stack
cout << “Is the stack full? ” << s.isFull() << endl;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
MAX SIZE of the array: 5
Insert elements in the stack:
Stack elements: 1 2 3 4 5
Is the stack full? 1
Remove an element from the stack! 1
Stack elements: 2 3 4 5
Is the stack full? 0
11. Write a C++ program that reverses the stack (using an array) elements.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10 // Maximum size of stack
class Stack {
private:
int top; // Index of top element
int st[MAX]; // Array to store elements
public:
Stack() {
top = -1; // Initialize top index to -1 (empty stack)
}
bool push(int x) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << “\nStack overflow” << endl; // Display message if stack is full
return false; // Return false to indicate failure in pushing element
}
st[++top] = x; // Increment top index and add element to array
return true; // Return true to indicate successful element addition
}
int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << “Stack underflow” << endl; // Display message if stack is empty
return 0; // Return 0 to indicate failure in popping element
}
return st[top–]; // Return top element and decrement top index
}
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << “Stack is empty” << endl; // Display message if stack is empty
return 0; // Return 0 to indicate failure in peeking element
}
return st[top]; // Return top element without modifying top index
}
bool isEmpty() {
return (top < 0); // Return true if stack is empty (top index is -1)
}
bool isFull() {
return (top >= MAX- 1); // Return true if stack is full (top index is equal to MAX – 1)
}
void display() {
if (top < 0) {
cout << “Stack is empty” << endl;
return;
}
cout << “\nStack elements: “;
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i–)
cout << st[i] << ” “;
cout << endl;
}
void reverse() {
int n = top + 1; // Get the number of elements in the stack
int tmp[MAX];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
tmp[i] = st[top–]; // Pop elements from the original stack and store them in the temporary array
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
push(tmp[i]); // Push the reversed elements back onto the original stack
}
}
};
int main() {
Stack stk; // Initialize the stack stk
//Insert elements in the stack:”;
stk.push(6);
stk.push(4);
stk.push(2);
stk.push(5);
stk.push(1);
stk.push(0);
stk.display(); // Display the elements of the stack
stk.reverse(); //Reverse the elements in the stack
cout<<“\nAfter reversing….: “;
stk.display(); // Display the reversed elements of the stack
cout << “\nRemove two elements:”;
stk.pop();
stk.pop();
stk.display(); // Display elements of the stack after popping
cout << “\nInsert two more elements”;
stk.push(7);
stk.push(10);
stk.display(); // Display elements of the stack after pushing
//Reverse the elements in the stack:”;
stk.reverse();
cout << “\nAfter reversing…..: “;
stk.display(); // Display the reversed elements of the stack after reversing again
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Stack elements: 0 1 5 2 4 6
After reversing….:
Stack elements: 6 4 2 5 1 0
Remove two elements:
Stack elements: 2 5 1 0
Insert two more elements
Stack elements: 10 7 2 5 1 0
After reversing…..:
Stack elements: 0 1 5 2 7 10

This website is an absolute gem! The content is incredibly well-researched, engaging, and valuable. I particularly enjoyed the [specific section] which provided unique insights I haven’t found elsewhere. Keep up the amazing work!
Thank you so much for your kind words…Thanks a lot